Understanding Real Estate Cycles: Historical Perspective
The best indicator to predict future market trends is to examine historical data. Below is the median sales price from 1987 to 2024.
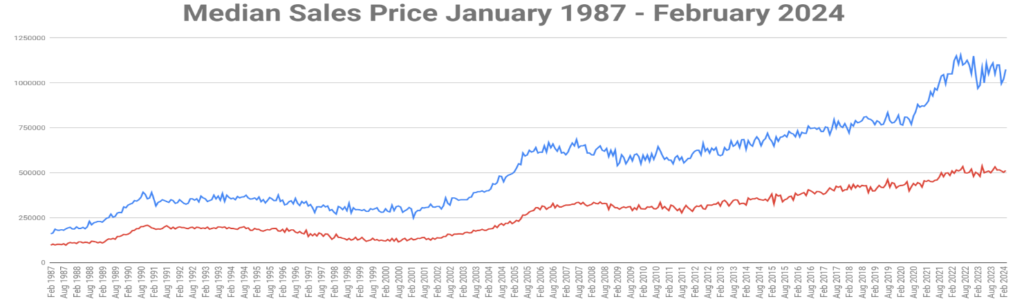
The real estate market goes in cycles of about 7-12 years. We will go over the Oahu real estate market cycles and what’s causing these cycles.
1980 – 1990: The Boom of Foreign Investment
During this period, the real estate market on Oahu saw a significant uptick in foreign investment particularly from Japan. This investment led to increasing property values and created a bullish market for sellers.
1990 -2000: Japanese Exodus & Stock Market Boom
The bubble burst in the 1990s when the Japanese economy crashed leading to Japanese investors pulling out of the U.S. real estate market. Housing prices dropped slightly. In addition, the stock market produced high returns leading many investors to shift from real estate to the booming stock market.
2000-2007: Stock Market Crash & Return to Real Estate
The dot-com bubble burst, and the stock market crashed. Investors began to consider real estate as a safer investment option. This was also the period of financial innovations, which were often predatory lending practices.
2007-2012: Housing Bubble
During the early 2000s, banks and financial institutions offered mortgages with increasingly lower credit requirements and initial payments. Many of these were subprime mortgages, aimed at borrowers with poor credit. There were also financial innovations like adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) and interest-only loans that allowed buyers to afford homes that were otherwise out of their reach based on traditional financing methods. These products often included terms that became financially burdensome when initial teaser rates expired. As adjustable mortgage rates reset at higher levels, many homeowners were unable to afford their mortgage payments leading to an increase in foreclosures. This increase in distressed sales added to the housing market supply without corresponding demand, causing home prices to plummet. The fall in home prices left many with mortgages that were larger than the value of their home(negative equity), which further fueled foreclosures and dropping home prices. In some places across America, home prices dropped 40,50 or even 60 percent.
2012-2020: Recovery and Growth
After the great recession in the previous period, the economy was in recovery mode. The Federal Reserve’s stimulates the economy by lowering interest rates. Lower rates make mortgages more affordable, encouraging buying activity in the housing market. As the economy recovered, employment levels improved, which increased consumer confidence. This translated to a higher demand for housing.
2020-2024: Covid-19 and It’s Aftermath
The pandemic profoundly impacted the housing market. During COVID-19, homeowners were generally reluctant to sell unless necessary, leading to a low supply of homes. However, demand surged for several reasons. Firstly, interest rates dropped below 3%, making mortgages more affordable. Secondly, lockdowns and the shift to remote work increased the value people placed on their living spaces, as they were spending more time at home. Many sought larger, more comfortable homes, thinking, “If I’m going to be stuck at home, I want a nicer, bigger place.” This combination of low supply and high demand caused home prices to soar, with many properties receiving dozens of offers and selling for well over the asking price.
Toward the end of 2022 and into 2023, the housing market entered a cooling phase after experiencing significant price increases in the preceding years. This rapid growth proved unsustainable, leading to a market correction. Concurrently, rising interest rates further contributed to the slowdown, as higher borrowing costs tempered buyer enthusiasm and reduced overall market activity.
